To-Do List Tutorial
1. Set Up the HTML Structure:
Below is the HTML structure for a basic to-do list:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>To-Do List</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>To-Do List</h1>
<form id="task-form">
<input type="text" id="task-input" placeholder="Add New Task">
<button type="submit">Add</button>
</form>
<ul id="task-list">
<!-- Tasks will be dynamically added here -->
</ul>
</div>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
2. Style the To-Do List (Optional):
You can style the to-do list using CSS. Below is a sample CSS file (styles.css) for basic styling:
/* styles.css */
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 20px auto;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
form {
margin-bottom: 20px;
display: flex;
}
#task-input {
flex: 1;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
background-color: #333;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #555;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
}
.task-item {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
padding: 10px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.task-item.completed {
text-decoration: line-through;
opacity: 0.6;
}
3. Handle Task Addition:
Here's the JavaScript code (script.js) to handle task addition:
// script.js
const taskForm = document.getElementById('task-form');
const taskInput = document.getElementById('task-input');
const taskList = document.getElementById('task-list');
taskForm.addEventListener('submit', addTask);
function addTask(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const taskText = taskInput.value.trim();
if (taskText !== '') {
const taskItem = document.createElement('li');
taskItem.className = 'task-item';
taskItem.textContent = taskText;
taskList.appendChild(taskItem);
taskInput.value = '';
}
}
4. Display Tasks:
This step is already covered by the code in step 3.
5. Handle Task Completion:
Here's the JavaScript code to handle task completion:
// script.js (continued)
taskList.addEventListener('click', completeTask);
function completeTask(event) {
const taskItem = event.target;
if (taskItem.tagName === 'LI') {
taskItem.classList.toggle('completed');
}
}
6. Handle Task Deletion:
Here's the JavaScript code to handle task deletion:
// script.js (continued)
taskList.addEventListener('contextmenu', deleteTask);
function deleteTask(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const taskItem = event.target;
if (taskItem.tagName === 'LI') {
taskItem.remove();
}
}
7. Store Tasks in Local Storage (Optional):
You can use local storage to store tasks. Below is the JavaScript code to store and retrieve tasks from local storage:
// script.js (continued)
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const tasks = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('tasks')) || [];
tasks.forEach(taskText => {
const taskItem = document.createElement('li');
taskItem.className = 'task-item';
taskItem.textContent = taskText;
taskList.appendChild(taskItem);
});
});
taskForm.addEventListener('submit', addTaskAndUpdateStorage);
function addTaskAndUpdateStorage(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const taskText = taskInput.value.trim();
if (taskText !== '') {
const taskItem = document.createElement('li');
taskItem.className = 'task-item';
taskItem.textContent = taskText;
taskList.appendChild(taskItem);
updateLocalStorage(taskText);
taskInput.value = '';
}
}
function updateLocalStorage(taskText) {
const tasks = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('tasks')) || [];
tasks.push(taskText);
localStorage.setItem('tasks', JSON.stringify(tasks));
}
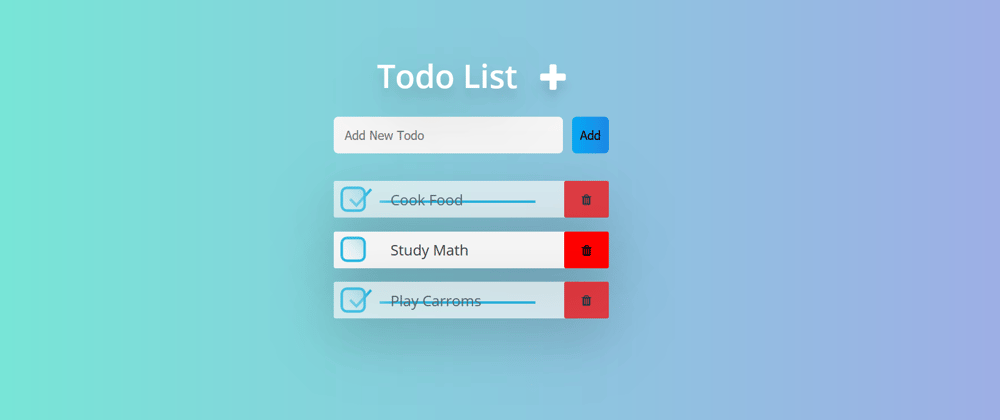
Output:
To-Do List

